
BASH FIND FILE BY OWNER CODE
Note that you must replace the with actual values in the following code examples to run the examples. Search results must meet at least one of the two conditions Furthermore, an OR link can be used or a condition can be negated: The pattern is matched against the file base name, excluding the directory. Here, a logical AND operation is implicitly assumed. Multiple patterns can be specified using a list. Several search parameters can also be combined. Below, you’ll find an overview of the most commonly used search parameters: This is followed by a space and the value of the parameter. A search parameter consists of a hyphen that is immediately followed by the name of the parameter.
BASH FIND FILE BY OWNER FREE
Plus, you can modify them with different options to fine-tune your search.ĭo you have any other tips and tricks for navigating Linux files and checking their ownership? If so, feel free to share them in the comments section below.First, the command itself is written, followed by a directory path, and a variable number of search parameters. All these commands are easy to use, so you can get the information you need in no time. One of the most useful features of the bash shell is the find command, the find command allows you to search for files or directories that meet specific. Get the Details You NeedĪs you can see, it’s not hard to find the file’s owner, group, and other relevant details of a file in Linux. If you want to change both the owner and group, type in “ chown username:groupname filename”. You can change the file’s group using the same function. So, for example, if you want Mark to be the owner of file123, you’ll type in “ chown mark file123.” But actually dont use ls for this, or really in scripts at all.

A better solution would replace grep with Awk instead, which has built-in support for examining only specific fields. Open the terminal and type in “ chown username filename”. The immediate problem with your attempt is the final which anchors the search to the end of the line, which is the end of the file name, not the owner field. If you want to change a file’s owner, you can use the chown command.
BASH FIND FILE BY OWNER HOW TO
Stat -c “%U %G” file123 How to Change the Owner of a File in Linux So if we use the file123 example again, the command will be: If you only want to see the file’s owner and group, you can use the %U and %G options. You can see the device on which the file is, who has access, when the most recent changes were made, etc. find directory -user root -perm -4000 -exec ls. Find files with setuid permissions by using the find command. All you have to do is type “ stat filename.” Become superuser or assume an equivalent role. You can input multiple file names and modify the command with many options showing you different information. The Stat is another highly useful command you can use to get many details on a file, including the owner.
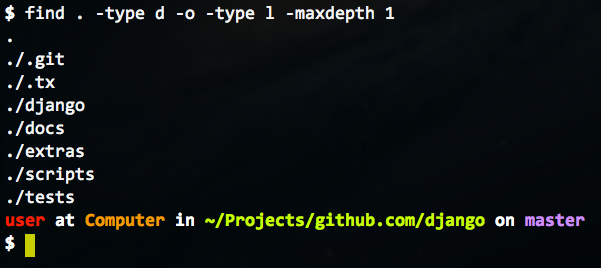
# find /dir -printf '%u:%g\n' | sort -t: -u Stat Command You can also use more advanced filtering to only show unique users by adding the -u option:įinally, you can see the group to which the file belongs by adding the %g option: You can do so with the following command syntax. But with the Print function, you can also list the files’ owners. People often use the Find command to look for files within a directory.
Of course, you’ll replace filename with the file’s actual name. Owner permissions The owners permissions determine what actions the owner of the file can perform on the file. Check the third column to see the owner.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
